the media resource function. Because
Instant Talk is a half-duplex service, the
media resource function must prevent two
or more users from sending media at the
same time. This is called talk burst control.
The MRF employs a request/response mech-
anism to control transmission rights. Users
who want to transmit must wait until their
requests have been granted. The MRF can
also revoke transmission rights when a user
abuses the service.
The HSS maintains the Instant Talk
subscriber profile by keeping track of the
core network node tasked with handling the
subscriber. An evolution of the home loca-
tion register (HLR) and the authentication
center (AUC) used by all IMS services, the
HSS also handles Instant Talk subscriber
authentication and authorization functions.
Instant Talk application server
The Instant Talk application server is basi-
cally a database tool that handles subscriber
data during call set-up
• to ensure that the called party is a sub-
scriber;
• to determine who is to be included in the
group during the call;
• to determine whether or not users have
activated Do-not-disturb mode; and
• to check whether the user has activated
manual or auto-answer mode.
The application server also stores and pass-
es down rules and regulations to the MRF.
Local policies stored in the application
server typically include timer values, such
as remaining talk time in a user’s account.
The Instant Talk application server also
supports group list management server
(GLMS) functionality, which enables users
with list management operations to create,
modify, retrieve and delete the groups and
contact lists needed for the Instant Talk ser-
vice. The GMLS also provides storage space
for groups and lists.
Client
Ericsson works with third parties to inte-
grate clients into terminals from different
vendors. Pre-integrated clients can be opti-
mized for the hardware platform on which
they run. For instance, to set its clients apart
from downloadable clients, Ericsson can
make use of the native voice codec imple-
mented for circuit-switched calls, to in-
crease performance and battery life.
To ensure maximum voice quality, even
in environments with limited bandwidth,
Ericsson employs the adaptive multirate
(AMR) codec and the enhanced variable rate
codec (EVRC). The AMR codec is used in
EDGE, GPRS and WCDMA terminals;
EVRC is used for CDMA2000 clients.
Besides SIP, Ericsson Instant Talk clients
use the real-time transport protocol (RTP)
to carry real-time data generated by the
voice codec. Frame bundling is used to
reduce the effect of relatively large headers
in the IP/UDP/RTP layers. This means that
several voice codec frames are sent in one
RTP packet. As dictated by IETF, the
18
Ericsson Review No. 1, 2004
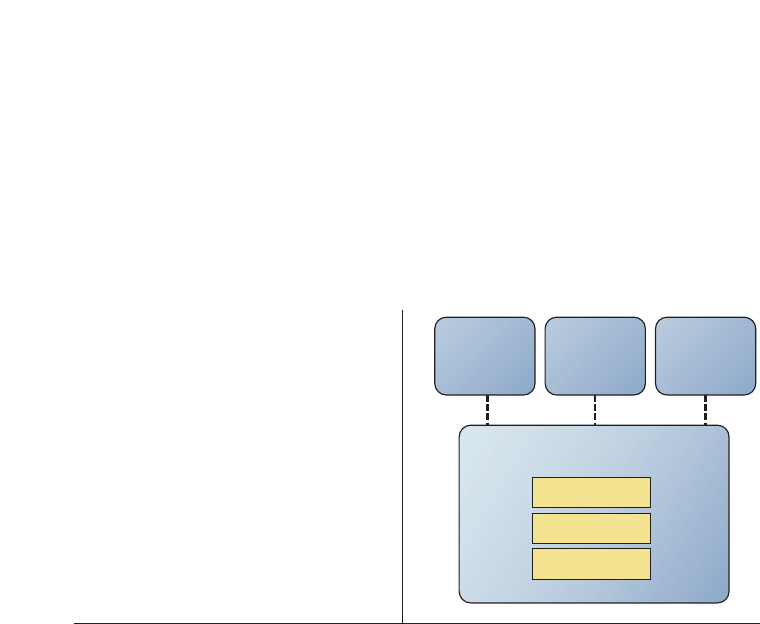
Ericsson
Instant Talk
Application
server
New service
#1
Application
server
IPMM
CSCF
HSS
MRF
New service
#2
Application
server
Figure 2
The IPMM system is built with service
evolution in mind.






